Introduction:
Many forex traders know all the technical indicators but still watch their profits evaporate when emotions take over. Have you ever blown a trade because you panicked or became overconfident? The core lesson from trading psychology is that mental strength is the “third candle” of trading. In fact, research shows that up to 90% of novice traders lose money, often due to emotional mistakes in trading rather than bad strategy. Studies confirm that traders who allow fear or greed to dominate tend to perform worse over time.
Trading success isn’t a magic gift, and staying calm is a skill you can definitely learn. This post covers forex psychology introduction and complete framework: scientific models, common traps, practical tools, and examples. We’ll show that trading is only 30% analysis and 70% mindset, so improving forex psychology is the key to consistent profits.
What is Trading Psychology?
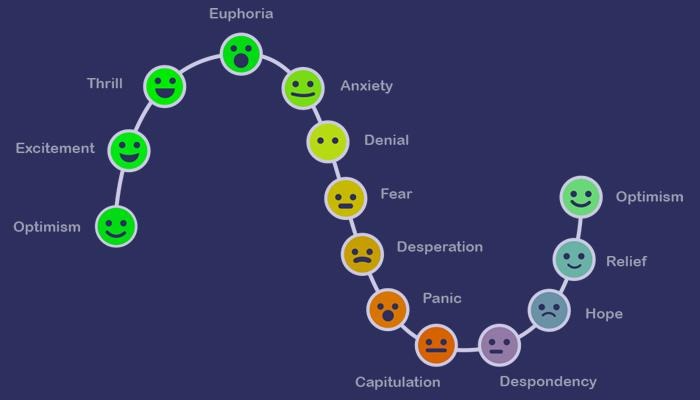
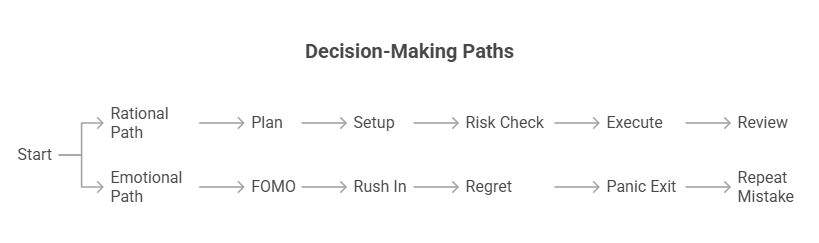
Trading psychology definition is simple. It is how a trader thinks, feels, and reacts when markets move. It’s about your mindset under pressure. Key emotions include greed, fear, hope, regret, anxiety, and FOMO (fear of missing out). Technical analysis is about reading the chart, whereas trading psychology is about reading yourself. For instance, think of it like learning a video game: when you play too eagerly just to win, you often make blunders. But being calm, composed and in control of your emotions allows you to put up an equal fight.
In “Trading in the Zone”, Mark Douglas stresses that a trader’s mindset can make or break performance. He notes that successful traders think in probabilities and accept risk calmly, while emotional traders see the market as out to get them. In practice, imagine a high-frequency trader who jumps out of winning trades at the slightest pullback because of fear. Over time, fear can cause underperformance. Controlling these emotional factors in forex trading, as well as negative biases, is just as important as any strategy. As Douglas says,
“To be confident, functioning in an environment where you can easily lose more than you intend to risk, requires absolute trust in yourself.”
Emotional Traps: Greed, Fear & Herd Mentality
Even smart strategies fail when emotions take over. Some common emotional trading traps include:
-
Greed: Chasing every big move, overleveraging, or “buying tops” because you “don’t want to miss out.” Greed tempts traders to risk too much on a single trade. In extreme cases, people double down on positions that are already huge, turning a small loss into a disaster.
-
Fear: Exiting winning trades too early or refusing to enter good setups because the market “might crash.” Fear can cripple performance by keeping you on the sidelines or locking in tiny gains. Many traders exit their positions the moment the market dips a bit, only to watch it rally shortly after.
-
Herd Mentality: Following the crowd. For example, seeing everyone on a chat group buy EUR/USD might make you do the same, often right before a reversal. Herd behavior can create bubbles that eventually pop.
-
Revenge Trading: After a loss, emotions run hot. One might immediately jump back in, risking even more, just to “win it back.” This is like a poker player who loses a big hand and then, in anger, goes “all in” irrationally on the next one.
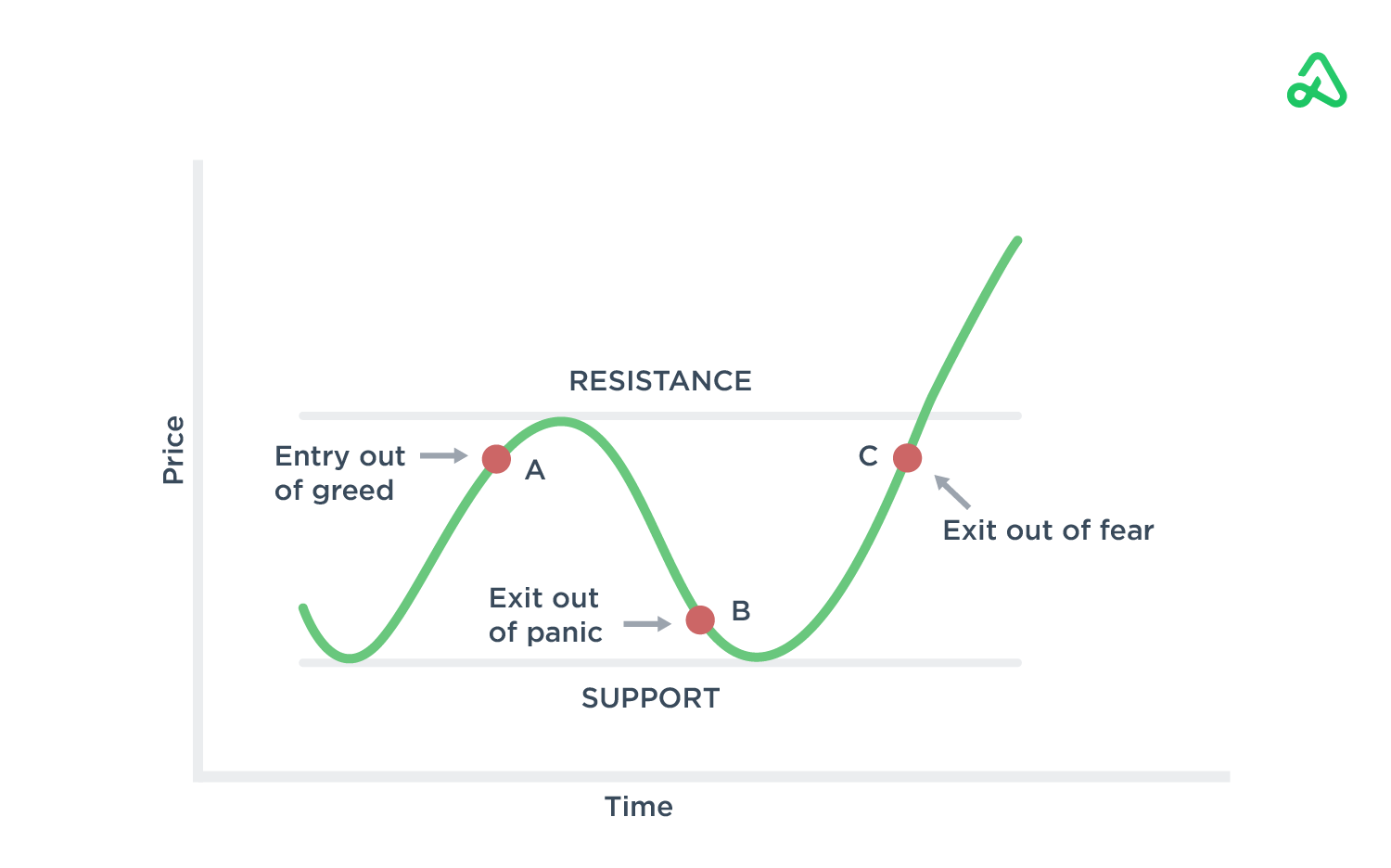
These traps distort rational decisions. The CNN Fear & Greed Index was even created because forex fear and greed are the two dominant emotions that swing markets. One recent example: after a big Fed announcement in 2022, many retail traders panicked and sold right into the bottom, just before the market rallied. In short, falling prey to emotional trading traps explains why so many traders fail.
A Scientific Look at Trading Emotions
Neuroscience and behavioral finance help explain why traders act the way they do. For instance, the amygdala is the brain’s fear center, which fires up when markets get volatile, triggering “fight or flight” reactions. This explains why a sudden crash can make us panic-sell; we instinctively want to run.
On the other hand, reward chemicals like dopamine play a role too. When you score a winning trade (or even just imagine one), your brain’s reward center lights up and releases dopamine. This creates a small “high” that reinforces the behavior, making trading feel addictive over time.
Behavioral economics adds more: Prospect Theory tells us that losses hurt about twice as much as gains feel good. In practice, this means traders are more upset by a $100 loss than happy about a $100 gain. Loss aversion in forex can cause irrational moves like holding onto losers or cutting winners too soon.
Stress and cognitive load also matter. Under high pressure, the brain becomes more impulsive. Neuroeconomics research shows that stress leads to shortcut thinking, which makes you rely on gut instinct instead of logic. This is why a chaotic trading day can wreak havoc on your judgment. Traders who use stop-losses routinely tend to protect their capital far better.
In short, understanding the neuroscience of trading confirms that strong emotions such as fear, greed, and addiction pathways skew decision-making. Recognizing these triggers is the first step to controlling them.
Does Your Personality Affect Your Trading Style?
Everyone has a unique personality, and some traders tailor strategies to fit. For example, analytical “big-picture” types (often INTJs, INTPs) prefer systematic swing or trend trading, while thrill-seekers (like ESTPs, ENTJs) gravitate toward fast-paced day trading. To know your trading personality type, ask yourself: Am I more rational or impulsive? Do I like strict rules or flexibility?
Most successful traders share a common trait: they tend to be more Intuitive (N) than Sensing (S). In MBTI terms, Intuitives enjoy finding patterns and predicting future moves, whereas sensing types prefer concrete, step-by-step tasks. In trading, Intuitives often excel at spotting big opportunities, while Sensers handle execution tasks reliably.
(Quick Self-Test):
-
Am I energized by quiet analysis or discussing the markets with others?
-
Do I prefer detailed data and routine or broad ideas and change?
-
Do I make decisions based on logic and plans or gut feeling and excitement?
Your answers can hint at a trading personality. The point is: use your strengths. Align your forex strategy by personality and temperament.
Practical Tools to Identify and Manage Emotions
Building emotional discipline requires concrete habits. A key tool is a trading journal. Keep a log of every trade, including your reasoning and feelings.
-
Was my last trade impulsive or well-planned?
-
Did I follow my trading plan or deviate?
-
Am I feeling anxious or overconfident right now?
Research shows traders who track their trades and emotions improve their results. Writing “I got greedy here” or “I panicked on that loss” next to a trade forces self-awareness.
Set firm rules for yourself. For example: after three losing trades in a row, stop trading for the day. This gives you a break to cool off instead of trading deeper losses. Similarly, use automatic tools: always place stop-loss and take-profit orders to lock in risk management. This removes the temptation to override your limits during stress.
Practice without real money: use a demo account. BTCDana, for example, offers a demo with $2,000 in virtual funds for practice. Finally, consider mindfulness techniques outside of trading: apps like Calm or Headspace can train you to notice stress and stay grounded. The goal of these tools is to make forex emotion management a habit.
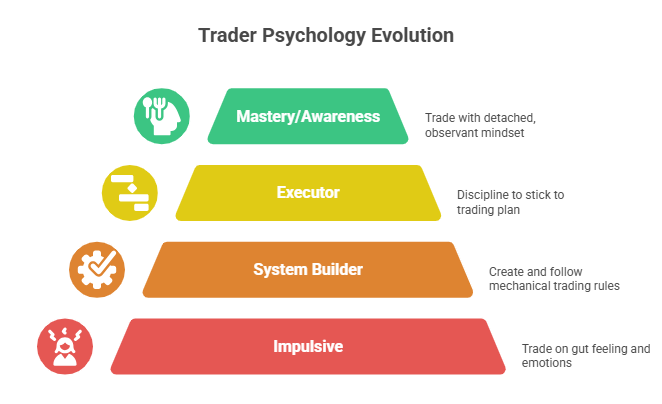
The Growth Path of a Calm Trader
Trader emotional maturity and personality typically evolve through stages as they master psychology:
-
Stage 1 – Impulsive: You trade on gut feeling or “tips”, riding emotional highs and lows
-
Stage 2 – System Builder: You create and write down rules (entry, exit, risk). You follow a mechanical system to build consistency.
-
Stage 3 – Executor: You discipline yourself to stick to the plan. You routinely use stops, size positions carefully, and review trades.
-
Stage 4 – Mastery/Awareness: You trade with a detached mindset. Emotions no longer drive you – you simply observe them.
Signs of progress include moving from “Why did I do that?!” to “What did I learn there?” at each loss. Trading mindset growth is a gradual journey: the key is patience and continuous refinement of your habits at each stage.
Platform Features That Support Emotional Discipline
A good risk control trading platform can reinforce these psychological habits. For example, BTCDana’s multi-asset app provides built-in tools to keep traders in check. It offers a demo account so you can practice rules without risk. Its interface lets you set auto stop-loss and take-profit orders, ensuring that plans are executed without hesitation. BTCDana also provides alerts and position limits: you can configure price alerts to avoid FOMO, or set a daily cap on trades (e.g. max 3 new positions) to prevent overtrading.
Other practical tips: use apps like Notion, Evernote, or even Excel for your journal, with reminders to fill it out. Set phone alerts before you enter a trade to pause and breathe. The idea is to let these forex trading tools enforce the discipline you want.
Common Pitfalls and Failure Case Studies
Even disciplined traders slip up. Here are some classic forex trading mistakes and how to prevent them:
-
Revenge Trading: Jumping right back into “win back” losses. This often means doubling your position out of anger, which usually creates even bigger losses.
Prevention: After a loss, step away. Take a break, review the journal, or switch to demo mode. Don’t trade until you’ve emotionally reset. -
Overpositioning: Betting too much of your account on one idea. Even if the setup is good, risking 20%+ of equity on one trade invites ruin.
Prevention: Always use a sensible position-size rule (e.g. risk 1–2% per trade) and stick to it. -
Copying Blindly: Following chatroom tips or unverified signals instead of your own plan. In one case, FTMO notes that copy-traders can waste accounts: “Too many signals… leads to unnecessary overtrading. The signal provider earns fees, but the trader ends up with zero in his account.”
Prevention: If you copy trades, do it in a demo first. Verify any strategy yourself. Always ask: Does this fit my plan?
Case Study – GameStop (2021): Hype on Reddit led many to buy at the peak; when the squeeze ended, late buyers were crushed. This shows how panic and greed (herding up, then out) can obliterate accounts.
Similarly, new traders have reported losing >90% of their demo equity by “mirroring” aggressive signals. The countermeasure in each case is clear: follow your own signal filters and risk rules, not the crowd.
The common thread is emotion. Recognizing these pitfalls in real examples reinforces the core lesson.
Conclusion and Action Steps
Trading is a mental game. You can’t control the market, but you can control and improve trading mindset. By keeping emotions in check, you tilt the odds in your favor. Mindset matters more than strategy.
Action Steps:
-
Start an Emotion Journal: Commit to writing down each trade’s rationale and your feelings.
-
Weekly Review: At week’s end, review your journal. Look for patterns. Adjust your plan or rules accordingly.
-
Practice on Demo: Open a free demo account on BTCDana and apply the same rules and journal process there. This lets you train discipline without risking capital.
By making psychological skill-building part of your routine, you steadily improve trading mindset. Trade smart, trade calm, and let rational strategy guide your path to profitability.