Once considered a niche trading method for a small segment of retail traders, Contract for Difference (CFD) trading has recently become far more popular with retail traders worldwide. But even for new traders, it is important to understand a very basic concept that lies at the heart of every CFD transaction: underlying assets. Whether you are a complete new trader about to take your first steps into CFD trading or an experienced trader looking to further enrich your knowledge of CFD trading, this guide will cover everything you need to know about underlying assets and the significant role they play in CFD trading.
What is an "Underlying Asset"?
An underlying asset is the instrument whose price directly affects the value of a CFD contract. Put simply, underlying assets are the "real" assets that your CFD is based on, even when you do not actually own that real asset when you buy CFD contracts.
To further demonstrate the concept of an underlying asset, think about a bet between you and a friend over the price and amount of apple juice they have. Specifically, you and your friend do not purchase any apple juice, however, you gain or lose money depending on what happens with the price of the apple juice. Now, in this example, the apple juice represents the underlying asset, and your "bet" is represented in your CFD contract.
Typical Types of Underlying Assets
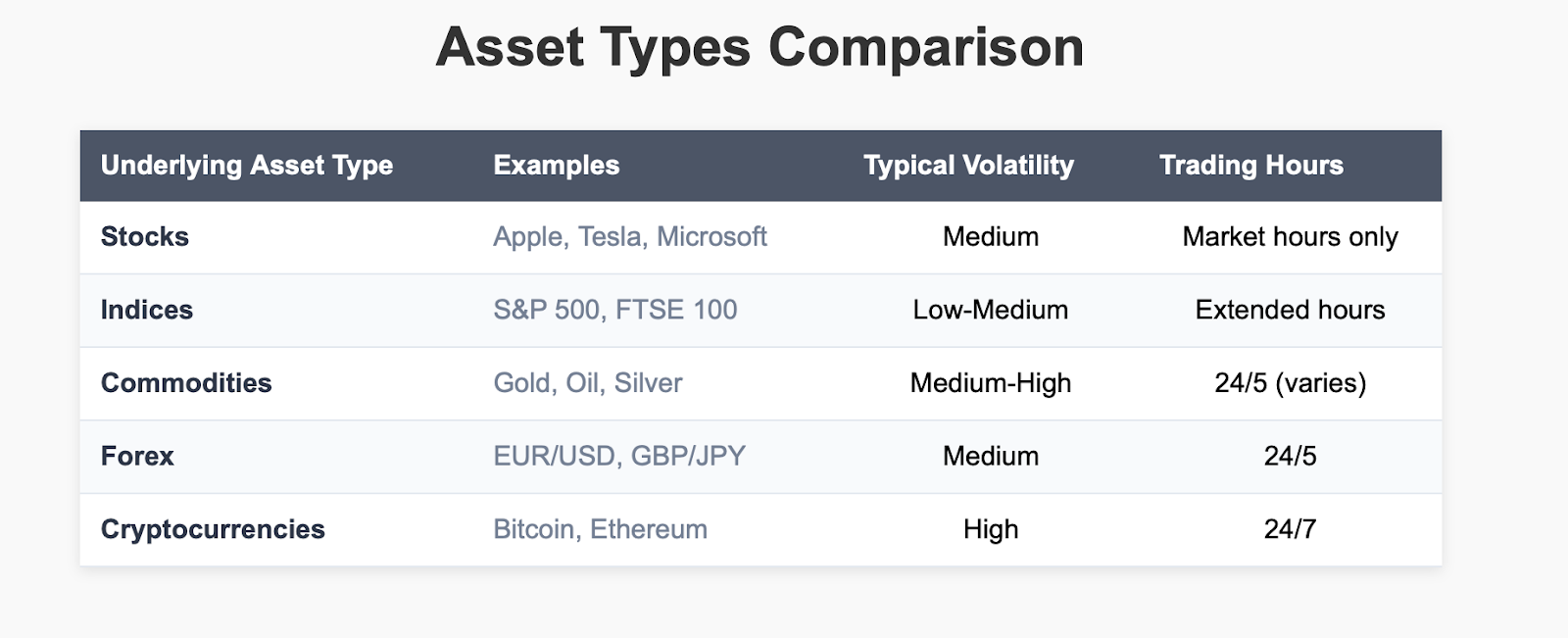
Many different types of CFD underlying assets can and do exist across many financial markets:
-
Stocks: Individual company's share such as Apple, Microsoft, Tesla, and Amazon
-
Indices: Market benchmarks such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones, FTSE 100, and Hang Seng Index
-
Commodities: Physical products such as gold, silver, crude oil, natural gas, and agricultural products
-
Currency Pairs: Foreign exchange pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and USD/CHF
-
Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin
Professional Example
When you trade a CFD on Apple stock, the actual share price of Apple on NASDAQ is your underlying asset. In the event Apple's share price goes up from $150 to $155, your apple CFD will cash out at a $5 increase in value as it would be expected as the CFD value typically reflects the underlying asset.
Why It's Important to Choose the Right Underlying Asset
The underlying asset that you choose determines your degree of risk exposure, returns, trading hours, and what factors could or may drive your trades. Some assets are very volatile (like cryptocurrencies) while others have lower degrees of volatility (like major stock indices). Understanding the correlation between the assets along with the price volatility differences is essential to a beginner trader's success in CFD trading.
Potentially misconstrued Key Point: The primary value of CFD trading is based on the price of the underlying asset; rather than the actual asset ownership.
Main Types of "Underlying Assets"
Learning about each of the different types of underlying assets is extremely important for a well-rounded trading methodology. Each category has its own set of characteristics affecting trading possibilities and levels of risk.
Stocks
A stock CFD is based on the stock of a company. You are speculating on the price movement of that firm's stock when trading a CFD on that stock.
-
Professional Example: When you trade a Microsoft CFD, your profits or losses depend on the actual Microsoft stock price movement on NASDAQ.
-
Simple Example: You can think of it like betting on whether your favorite company (example) will get a good or bad "report card" (earnings) and whether it will hurt the company's "popularity" (share price).
Characteristics: moderate volatility affected by company news, financial reporting, and the performance of the sector.
Indices
Index CFDs replicate the performance of a basket of stocks that are meant to illustrate a certain market or sector of the economy.
-
Professional Example: S&P 500 CFD tracks the performance of a combined market value of 500 large-cap companies in the USA.
-
Simple Example: Imagine betting against the average score of the top 500 students in the country - that's like index trading.
Characteristics: Lower volatility than single stocks, broader market opportunity, diversification in your portfolio.
Commodities
Commodity CFDs are based around raw materials and losses in commodity trading, typical agricultural products.
-
Professional Example: The prices of a gold CFD change at a price based on the pure gold spot price in the international market at that time.
-
Simple Example: This is like trying to predict whether the price of wheat at your local market goes up or down during harvest season.
Characteristics: High volatility, supply/demand based trading, influenced by weather, geopolitical elements, and economic situations.
Currency pairs
With Forex CFDs, you are trading one currency against another.
-
Professional Example: An EUR/USD CFD profits when the Euro gets stronger against the US dollar.
-
Simple Example: Think about buying currency before you go overseas and hoping while you are away your home currency gets stronger.
Characteristics: Very liquid, 24/5, and influenced by economic data and central bank policies.
Cryptocurrencies
Crypto CFDs mirror the pricing of the respective digital currency and do not require you to be in possession of actual cryptocurrency.
-
Professional Example: A Bitcoin CFD allows you to speculate on the price of Bitcoin without worrying about digital timeframes or wallets.
-
Simple Example: You are betting that digital "gold" (Bitcoin) will be worth more at a future point without being able to own it.
Characteristics: Extremely volatile, 24/7, and driven by adoption, regulation and sentiment.
Volatility Comparison
Gold tends to have steady price movements that occasionally spike based on economic uncertainty while Bitcoin can experience price fluctuations of 10-20% in a day making Bitcoin CFDs potentially much more profitable but also way more risky than gold CFDs.
How Underlying Asset Prices Influence CFD Trading
The connection between underlying asset prices and CFD trading outcomes is direct and obvious. Knowing how to take advantage of this connection will help you manage your risk and maximize your profits.
Direct price linking
CFD prices follow the underlying asset prices almost directly. When the underlying asset's price moves, so does your CFD position, including profit or loss.
Long vs Short positions
Long position (Buy): You profit when the underlying asset price increases
Short position (Sell): You profit when the underlying asset price decreases
Professional Example
Let’s say you buy a CFD on Tesla shares at $200, for a position size of 100 shares. If Tesla shares increase to a value of $210, your profit is $10 per share x 100 shares = $1,000 (not including any fees or spreads).
Simple Example
Now let’s think about apple juice. If you "bet" that the price of apple juice was going to increase from $5 to $6 per bottle and you "bet" on 100 bottles, you earn $1 x 100 = $100 if you were correct.
Leverage Multiplication
Leverage multiplies both profit and loss. So with 10:1 leverage, if the underlying asset moved 1%, your account balance would change 10%.
Example: You have $1,000 with 10:1 leverage, or $10,000 worth of crude oil CFD. This means a 5% increase in oil prices gives you a $500 profit (50% return on your $1,000), and a 5% decrease gives you a $500 loss.
How to Choose an Underlying Asset
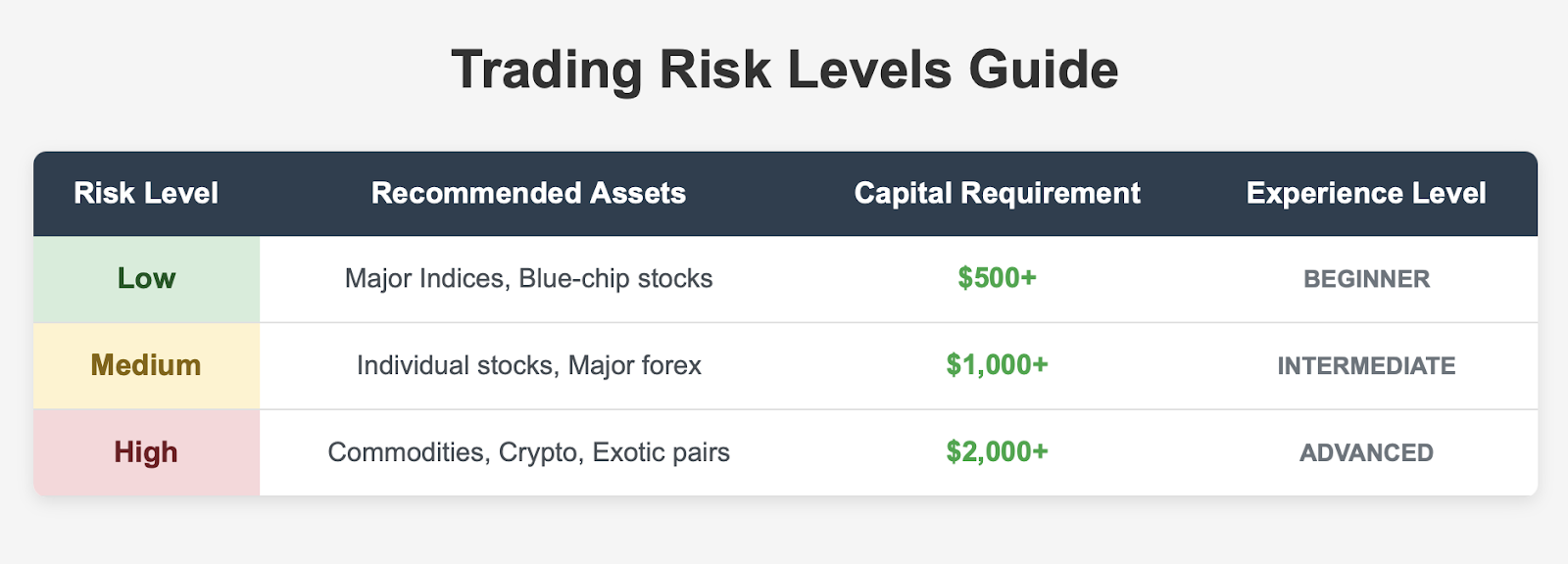
Given that choosing appropriate underlying assets is one of the most critical choices in CFD trading, you want to select one that is consistent with your risk tolerance, trading experience, available trading capital, and time commitment.
Risk Tolerance Considerations
Conservative Traders: Major stock indices (S&P 500, FTSE 100) tend to be less volatile than other assets and usually demonstrate a more predictable, steady price flow.
Moderate Risk Traders: A selection of individual blue-chip stocks and major currency pairs will balance your risk-to-reward ratio.
Aggressive Traders: More volatile assets such as commodities, emerging market and second-tier level assets, and cryptocurrency will provide volatility and profit opportunities.
Considering How Much Time You'll Devote to Trading
Day Traders: You would want to focus on underlying assets that have high liquidity like the major forex pairs, popular individual stocks, and indices with tight spreads.
Swing Traders: You would want to consider commodities and individual stocks that you are watching and provide clear technical patterns over a period of days or weeks.
Position Traders: You would want to see indices or stocks with reasonably stable price movements as that is what you are looking for in developing your trend based trading position.
Capital Amounts
Small Amounts (e.g. $500-$2,000): You can focus on major currency pairs or index CFDs that have smaller minimum position sizes.
Medium Amounts (e.g. $2,000-$10,000): These amounts allow you to expand your exposure to additional asset classes, including individual stocks and commodities.
Larger Amounts (e.g. $10,000+): You will have options to trade any underlying asset type while maintaining adequate risk management.
Example That’s Easy to Follow
An example of the types of trade that a new trader with medium risk tolerance who is using a trading application like BTCDana might make would be on the Hang Seng Index CFDs because:
-
Lower volatility than individual stocks;
-
A regulated market with predictable trading hours;
-
Minimum asset research and analysis required;
-
What you trade represents diversified exposure to the Hong Kong market.
Platform Considerations
When you use a trading application like BTCDana, as a trader, you can screen underlying assets:
-
By volatility;
-
By volume;
-
By spread;
-
Obtain extensive information and historical charts on various assets;
-
Experiment on different asset types via demo accounts;
-
And receive appropriate market analysis and signals.
The Relation between the Underlying Asset and CFD Contract
Understanding the relationship between CFD contracts and their underlying assets is a key concept to understanding CFD trading and avoid misconceptions.
CFD as a Derivative Contract
As a derivative financial instrument, the value of the CFD contract is determined from the underlying asset price. However, the CFD contract does not convey ownership of the underlying asset and is simply a contract where you agree to exchange the price difference between when you opened a position and when you closed it.
You Don't Own The Asset
When you trade CFDs, you are never the actual owner of the underlying asset.
This means:
-
No vote with stock CFDs
-
No physical deliveries of commodities
-
No true cryptocurrencies in your wallet
-
No dividends (some brokers provide adjustments for dividends)
Professional Outlook
When you trade gold CFDs you are speculating on the price of gold, and you don't have gold. You don't have to worry about storing, insuring, or authenticity of the gold. All you care about is
Simple Example
Think about making a friendly bet with a friend about whether the price of apple juice is going to go up or down in the following week. You are not buying apple juice, and you are not selling apple juice. You are just agreeing to pay each other the difference, based on price fluctuations. This is how CFDs work.
-
Contract details: Each CFD contract has details that relate to the underlying asset.
-
Contract size: How much of the underlying asset a CFD represents
-
Minimum price movement: The smallest price fluctuation that will affect your position
-
Trading sessions: When can you enter and exit positions
-
Margin: The amount of capital required to be held against the position
Sample BTCDana Platform
A gold CFD on BTCDana may equal 100 ounces of gold. This means if gold increases in price from $1,800 to $1,805 per ounce, then your position will move from $0 to $500 (this does not take leverage into account).
It is this derivative nature of the product which permits CFD trading to create some key positives: no need for large sums of money to secure highly priced assets, profit from falling prices, and access to global markets via one platform.
Factors Affecting Underlying Asset Price Movements
For your CFD trading to be successful, it is paramount to be able to understand those basic macro and micro dynamics producing price movement in your chosen underlying asset. Each of the main asset classes are impacted differently by varying economic, political, and other market related factors.
Macroeconomic Data
To start, economic data is a major contributor when it comes to changes in prices of all asset categories:
-
GDP Growth: Sustained periods of growth typically advance stock indices and currency price movements while causing valuations of safe haven assets like gold to weaken.
-
Employment Data: Strength or weakness in the job market will have a positive/negative impact on currencies as well as current market sentiment with respect to indices like the S&P 500.
-
Inflation Reports: Inflation increases, when declared, will have a positive impact on commodities prices, while causing weakness in currencies like the U.S. dollar.
Central Bank Policies
Interest Rate Decisions: Rate changes directly affect currency pairs and indirectly influence stocks and commodities.
Quantitative Easing: Money printing policies can weaken currencies while boosting asset prices.
Forward Guidance: Central bank communication about future policy affects market expectations.
Geopolitical Events
Wars and Conflicts: Typically boost safe-haven assets (gold, Swiss franc, Japanese yen) while pressuring risk assets.
Trade Wars: Tariffs and trade disputes affect specific currencies and stock sectors.
Sanctions: International sanctions can dramatically impact targeted countries' assets and related commodities.
Industry-Specific Factors
Supply and Demand: Particularly important for commodity CFDs.
-
Oil: OPEC decisions, shale production, seasonal demand
-
Gold: Central bank buying, jewelry demand, mining supply
-
Agricultural: Weather, harvest cycles, global food demand
Company-Specific News: For stock CFDs:
-
Earnings reports and guidance
-
Management changes
-
Product launches or failures
-
Regulatory approvals or setbacks
Professional Example
US Nonfarm Payroll data release showing unexpectedly strong job growth could:
-
Strengthen USD against other currencies (affecting EUR/USD, GBP/USD CFDs)
-
Pressure gold prices as dollar strength reduces gold's appeal
-
Boost US stock indices as strong employment suggests economic health
Simple Example
Think of how local news affects prices in your neighborhood. If a new factory opens (good economic news), local property values might rise. If there's a scandal about the mayor (political uncertainty), people might be more cautious about spending. Global markets work similarly but on a much larger scale.
Market Sentiment Factors
Risk Appetite: During "risk-on" periods, investors favor stocks and higher-yielding currencies. During "risk-off" periods, they prefer safe havens.
Technical Levels: Key support and resistance levels can trigger significant price movements regardless of fundamental factors.
Seasonal Patterns: Some assets show predictable seasonal trends (like agricultural commodities or tourism-related currencies).
Understanding these factors helps traders:
-
Anticipate potential price movements
-
Plan trades around major economic releases
-
Manage risk during volatile periods
-
Identify opportunities across different asset classes
Conclusion and Actionable Tips
Understanding the notion of underlying assets is essential for success in your CFD trading. In this guide, we've discussed how underlying assets are the basis on which all CFD trades are made, the ability of underlying assets to have a direct impact on your potential profits and losses, as well as the risks which these underlying assets will determine in your trading portfolio.
Key Learnings
Knowing this understanding of underlying assets will enable you to:
-
Choose which markets to trade from an informed position
-
Consider risk levels that are suitable to your skills set and capital
-
Consider what drives price changes in different asset classes
-
Formulate trading strategies based on the characteristics of underlying assets
Getting Started: Actionable Steps
1. Start with Education: prior to putting your hard earned money on the line and trading underlying assets in your CFDs or otherwise, you will want to fully understand what underlying assets you are going to trade. Take advantage of the educational resources available, look at market analysis, and consider economic calendars.
2. Use Demo Trading First: Practice in demo trading using the different underlying assets available to you on BTCDana's demo trading platform, until you thoroughly understand how different underlying assets behave without risking any money.
3. Start Small and Diversify: Start by using very small position sizes established across several different asset classes for experience while each position size is ultimately relatively small.
4. Plan for Risk Management: Never risk more than you can afford to lose, and always use stop-loss orders to protect your capital.
Recommended Learning Path
-
Week 1-2: Learn about major index CFDs with large market caps and low volatility
-
Week 3-4: Learn about individual stock CFDs for companies that you are familiar with
-
Week 5-6: Learn about major currency pairs during good trading times
-
Week 7-8: Look for commodity CFDs after establishing a solid risk management plan.
-
Week 9+: Advanced traders can look to CFD cryptocurrencies.
Benefits of the Dedicated And Comprehensive Tools Offered By the BTCDana Platform
The BTCDana platform includes large array of tools that can help you analyze the underlying assets:
- Real time price feeds and charts
- An economic calendar identifies major news events impacting your selected asset
- A dedicated risk management tool with the ability to institute stop-loss or take-profit orders
- An education menu consisting of a detailed glossary, video explanations, and market commentary
- The ability to open Demo Accounts for practice (risk-free) using real-time price data.
Are You Ready to Begin Trading CFDs?
Start your journey into CFD trading by opening a BTCDana demo account and use it to practice trading underlying assets, refine your trading skills, and gain confidence prior to trading live. You now have the background knowledge about all underlying assets to begin practicing CFD trading!
Register for your free BTCDana demo account today and start your exploration of CFD underlying assets risk-free